Biofilm – Constant source of microorganisms & potentially pathogens
What is Biofilm?
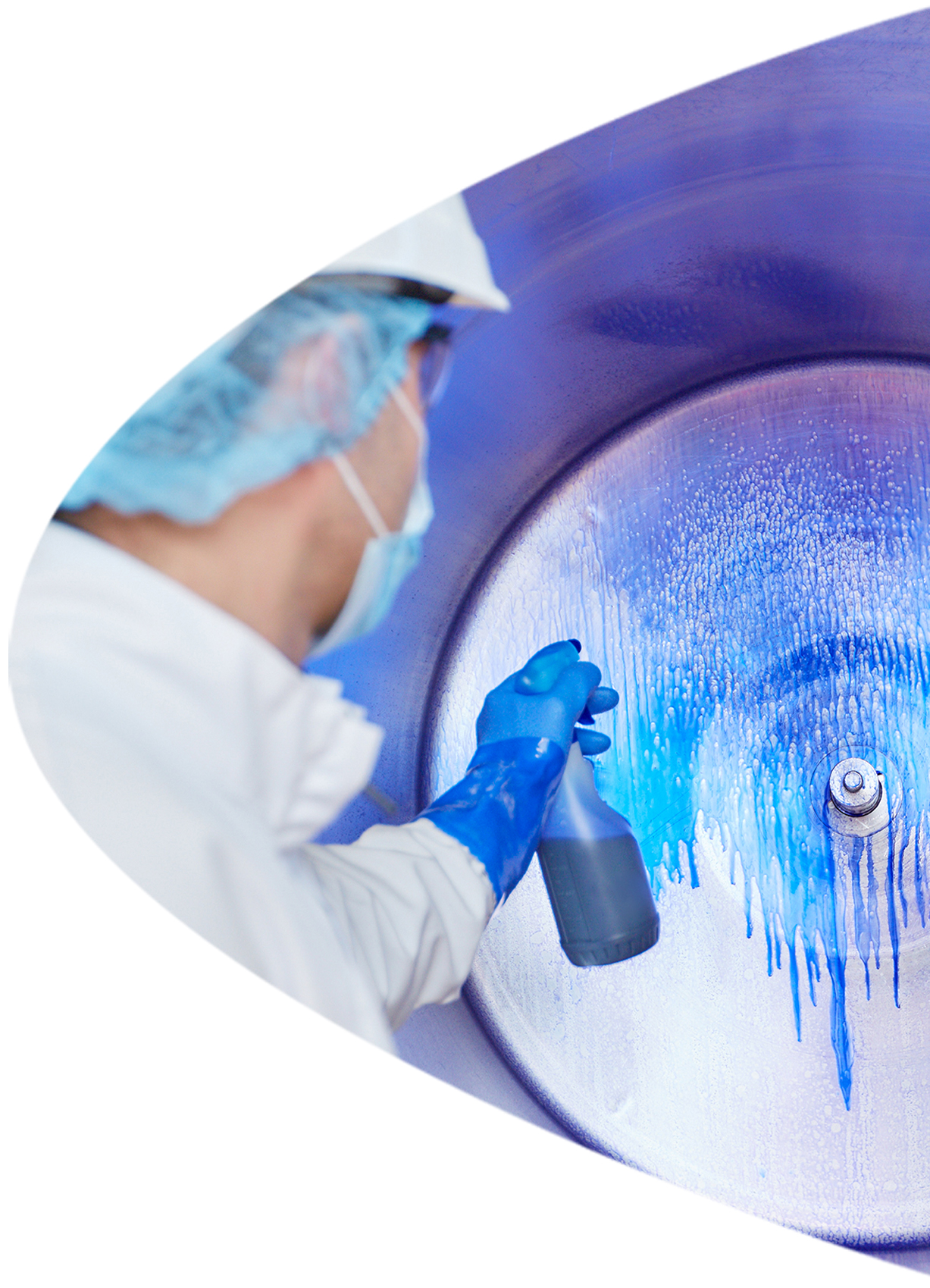
Biofilms are complex communities of microorganisms that adhere to surfaces and are surrounded by a matrix of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS). EPS plays a crucial role in the formation, stability, and protection of biofilms.
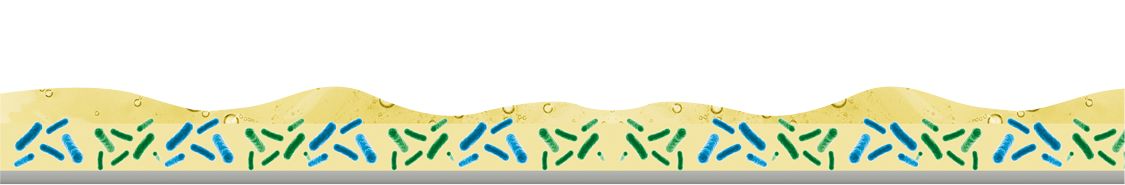
Depending on the environmental condition, biofilm can be made up of Listeria monocytogenes, Bacillus cereus and mycoïdes, Salmonella spp., Campylobacter, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Leuconostoc or Cronobacter (Enterobacter sakazakii) building the biofilm matrix (organic polymers, polysaccharides, proteins, DNA, lipids etc.) and other (pathogen) microorganisms, phages, spoiling enzymes, spores, molds and yeast which are living inside the matrix.
Thanks to this structure, biofilms way more resistant to biocidal substances compared to the same bacteria in a liquid medium. This complex construction ensures survival even in extreme conditions.